Posted by Kanhaiya
The Spring Framework is a popular open source application framework that can make Java EE development easier. It consists of a container, a framework for managing components, and a set of snap-in services for web user interfaces, transactions, and persistence. A part of the Spring Framework is Spring Web MVC, an extensible MVC framework for creating web applications.
Introduction to Spring Web MVC framework:-
Spring MVC is the web component of Spring’s framework. It provides a rich functionality for building robust Web Applications. The Spring MVC Framework is architected and designed in such a way that every piece of logic and functionality is highly configurable. Also Spring can integrate effortlessly with other popular Web Frameworks like Struts, WebWork, Java Server Faces and Tapestry. It means that you can even instruct Spring to use any one of the Web Frameworks. More than that Spring is not tightly coupled with Servlets or JSP to render the View to the Clients. Integration with other View technologies like Velocity, Freemarker.
In Spring Web MVC you can use any object as a command or form-backing object; you do not need to implement a framework-specific interface or base class. Spring’s data binding is highly flexible: for example, it treats type mismatches as validation errors that can be evaluated by the application, not as system errors. Thus you need not duplicate your business objects’ properties as simple, untyped strings in your form objects simply to handle invalid submissions, or to convert the Strings properly. Instead, it is often preferable to bind directly to your business objects.
Following is the Request process lifecycle of Spring 3.0 MVC:-
Model view controller is a software architecture design pattern. It provides solution to layer an application by separating three concerns business, presentation and control flow.
Advantages of Spring MVC Framework:-
Spring 3 MVC Basic Architecture:-
The Spring web MVC framework provides model-view-controller architecture and ready components that can be used to develop flexible and loosely coupled web applications. The MVC pattern results in separating the different aspects of the application (input logic, business logic, and UI logic), while providing a loose coupling between these elements.
In Spring 3 MVC framework Dispatcher Servlet access Front Controller which handles all coming requests and queses for forward to the different controller.
MultipartResolver:-
Spring has built-in multipart support to handle file uploads in web applications. By default, no multipart handling will be done by spring framework. The spring framework will only track for the multipart requests only when there is a component of type MultipartResolver is registered in the spring mvc configuration file.
LocaleResolver:-
Spring has a wonderful support for the Internationalization. The DispatcherServlet enables to automatically resolve the locale in the request. This is done using the LocaleResolver component. The different LocaleResolvers implementations are AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver, CookieLocaleResolver, SessionLocaleResovler etc., These components scan the request headers, cookies and session for the locale respectively.
ThemeResolver-
This component is used to apply different CSS based on the request and the current theme.
HandlerMapping-
This component decides on what controllers method needs to be invoked when a request with a HTTP Method arrives. Based on this components response, the DispatcherServlet will invoke the Controllers handler method.
HandlerAdapter-
Spring MVC gives support to handle the request to the Actions/Controllers of other MVC Frameworks. This component is not for the application developer. This is implemented by the advanced users who want to have their own flow for the request in the framework.
HandlerExceptionResolver-
This component helps to check if there are any exceptions that have occurred during the request processing and if picks the respective view configured for that exception and forwards it to the client.
RequestToViewNameTransaltor-
The RequestToViewNameTranslator helps to transform the URL of the incoming request to a view name.
ViewResolver-
This component plays a vital role in deciding on the view type that needs to be sent and also prepares the view.
All the above mentioned components ie. HandlerMapping, Controller and ViewResolver are parts of WebApplicationContext which is an extension of the plain ApplicationContext with some extra features for web applications.
Required Spring 3.0 MVC Configuration:-
Consider the following DispatcherServlet servlet configuration (in the web.xml file)
Defining a Controller:-
As an example, with JSP as a view technology, you can use the UrlBasedViewResolver. This view resolver translates a view name to a URL and hands the request over to the RequestDispatcher to render the view.
Spring Web MVC Framework Examples:-
Reference
Web MVC framework
The Spring Framework is a popular open source application framework that can make Java EE development easier. It consists of a container, a framework for managing components, and a set of snap-in services for web user interfaces, transactions, and persistence. A part of the Spring Framework is Spring Web MVC, an extensible MVC framework for creating web applications.
Introduction to Spring Web MVC framework:-
Spring MVC is the web component of Spring’s framework. It provides a rich functionality for building robust Web Applications. The Spring MVC Framework is architected and designed in such a way that every piece of logic and functionality is highly configurable. Also Spring can integrate effortlessly with other popular Web Frameworks like Struts, WebWork, Java Server Faces and Tapestry. It means that you can even instruct Spring to use any one of the Web Frameworks. More than that Spring is not tightly coupled with Servlets or JSP to render the View to the Clients. Integration with other View technologies like Velocity, Freemarker.
Request Processing Lifecycle
In Spring Web MVC you can use any object as a command or form-backing object; you do not need to implement a framework-specific interface or base class. Spring’s data binding is highly flexible: for example, it treats type mismatches as validation errors that can be evaluated by the application, not as system errors. Thus you need not duplicate your business objects’ properties as simple, untyped strings in your form objects simply to handle invalid submissions, or to convert the Strings properly. Instead, it is often preferable to bind directly to your business objects.
Following is the Request process lifecycle of Spring 3.0 MVC:-
- The client sends a request to web container in the form of http request.
- This incoming request is intercepted by Front controller (DispatcherServlet) and it will then tries to find out appropriate Handler Mappings.
- With the help of Handler Mappings, the DispatcherServlet will dispatch the request to appropriate Controller.
- The Controller tries to process the request and returns the Model and View object in form ofModelAndView instance to the Front Controller.
- The Front Controller then tries to resolve the View (which can be JSP, Freemarker, Velocity etc) by consulting the View Resolver object.
- The selected view is then rendered back to client
- Powerful and straightforward configuration of both framework and application classes as JavaBeans. This configuration capability includes easy referencing across contexts, such as from web controllers to business objects and validators.
- Adaptability, non-intrusiveness, and flexibility. Define any controller method signature you need, possibly using one of the parameter annotations (such as @RequestParam, @RequestHeader, @PathVariable, and more) for a given scenario.
- Reusable business code, no need for duplication. Use existing business objects as command or form objects instead of mirroring them to extend a particular framework base class.
- Customizable binding and validation. Type mismatches as application-level validation errors that keep the offending value, localized date and number binding, and so on instead of String-only form objects with manual parsing and conversion to business objects.
- Customizable handler mapping and view resolution. Handler mapping and view resolution strategies range from simple URL-based configuration, to sophisticated, purpose-built resolution strategies. Spring is more flexible than web MVC frameworks that mandate a particular technique.
- Flexible model transfer. Model transfer with a name/value Map supports easy integration with any view technology.
- Customizable locale and theme resolution, support for JSPs with or without Spring tag library, support for JSTL, support for Velocity without the need for extra bridges, and so on.
- A simple yet powerful JSP tag library known as the Spring tag library that provides support for features such as data binding and themes. The custom tags allow for maximum flexibility in terms of markup code.
- Beans whose lifecycle is scoped to the current HTTP request or HTTP Session. This is not a specific feature of Spring MVC itself, but rather of the WebApplicationContext container(s) that Spring MVC uses.
Model view controller is a software architecture design pattern. It provides solution to layer an application by separating three concerns business, presentation and control flow.
- Model can be some DAO layer or some Service Layers which give some information about request or requested information or Model can be a POJO which encapsulates the application data given by the controller.
- View is responsible for rendering the model data and in general it generates HTML output that the client's browser can interpret.
- Controller is responsible for processing user requests and building appropriate model and passes it to the view for rendering.
Advantages of Spring MVC Framework:-
- Supports RESTful URLs.
- Provide a very clean division between controllers, JavaBean models, and views.
- Annotation based configuration(i.e. you may reduce the metadata file or less of configuration).
- Supports to plug with other MVC frameworks like Struts, Struts2, WebWorks etc.
- Flexible in supporting different view types like JSP, velocity, XML, PDF, Tiles etc.
- It initialize the framework to cater to the requests.
- Load the map of all URLs and the components responsible to handle the request.
- Prepare the map for the views.
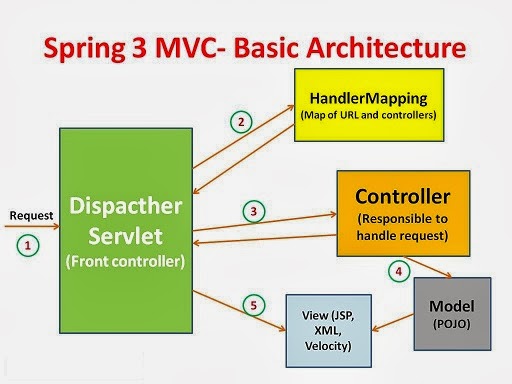
Spring 3 MVC Basic Architecture:-
The Spring web MVC framework provides model-view-controller architecture and ready components that can be used to develop flexible and loosely coupled web applications. The MVC pattern results in separating the different aspects of the application (input logic, business logic, and UI logic), while providing a loose coupling between these elements.
In Spring 3 MVC framework Dispatcher Servlet access Front Controller which handles all coming requests and queses for forward to the different controller.
- Whenever request lands the dispatcher servlet consult with HandlerMapping (HandlerMapping- is a component which have the map of URL and Controller which need to be invoked for that particular request which lands with URL)
- Then Dispatcher servlet has information about which is controller need to be invoked.
- Then that controller will be invoked.
- Then Controller can request the model for some information. (about some DAO, Service layer or Data in POJO, or data in database using business logic)
- Once process has been done then dispatcher servlet get the response then dispatcher servlet will get view resolver to build the view and view resolver look out what view has being configured it has been JSP, Velocity, XML etc. based this configuratin view has been prepared and the information from model i.e. POJO it will be put on the view and response will be send back to browser.
- Request lands to Front Controller i.e. DispatcherServlet
- Capture the Request Locale i.e use for internationalization i.e Read .properties files
- Then check for multipart-file(MIME type header or not) upload data from distributed application
- Then consult with HandlerMapping for which Controller to be invoked
- Then responsibility is given to the Handler Chain
- This Handler Chain is responsible to be invoked some of the interceptors that needs to be invoked before of a controller and after the controller that means interceptors are here like very to similar to the filters that help to separate the pre-process logic and post-process logic.
- After process of pre-process interceptor return to the controller process the post-process logic.
- Then return to the view resolver prepared the view based on your configuration decide the which configuration (JSP, Velocity, PDF etc.) to be invoked.
- After choosing view technology prepare the view and return the response back to the client.
MultipartResolver:-
Spring has built-in multipart support to handle file uploads in web applications. By default, no multipart handling will be done by spring framework. The spring framework will only track for the multipart requests only when there is a component of type MultipartResolver is registered in the spring mvc configuration file.
LocaleResolver:-
Spring has a wonderful support for the Internationalization. The DispatcherServlet enables to automatically resolve the locale in the request. This is done using the LocaleResolver component. The different LocaleResolvers implementations are AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver, CookieLocaleResolver, SessionLocaleResovler etc., These components scan the request headers, cookies and session for the locale respectively.
ThemeResolver-
This component is used to apply different CSS based on the request and the current theme.
HandlerMapping-
This component decides on what controllers method needs to be invoked when a request with a HTTP Method arrives. Based on this components response, the DispatcherServlet will invoke the Controllers handler method.
HandlerAdapter-
Spring MVC gives support to handle the request to the Actions/Controllers of other MVC Frameworks. This component is not for the application developer. This is implemented by the advanced users who want to have their own flow for the request in the framework.
HandlerExceptionResolver-
This component helps to check if there are any exceptions that have occurred during the request processing and if picks the respective view configured for that exception and forwards it to the client.
RequestToViewNameTransaltor-
The RequestToViewNameTranslator helps to transform the URL of the incoming request to a view name.
ViewResolver-
This component plays a vital role in deciding on the view type that needs to be sent and also prepares the view.
All the above mentioned components ie. HandlerMapping, Controller and ViewResolver are parts of WebApplicationContext which is an extension of the plain ApplicationContext with some extra features for web applications.
Required Spring 3.0 MVC Configuration:-
Consider the following DispatcherServlet servlet configuration (in the web.xml file)
With the above servlet configuration in place, you will need to have a file called /WEB-INF/golfing-servlet.xml in your application; this file will contain all of your Spring Web MVC-specific components (beans). You can change the exact location of this configuration file through a servlet initialization parameter.golfing org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet 1 golfing /golfing/*
Defining a Controller:-
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping("/helloWorld")
public ModelAndView helloWorld() {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
mav.setViewName("helloWorld");
mav.addObject("message", "Hello World!");
return mav;
}
}
As an example, with JSP as a view technology, you can use the UrlBasedViewResolver. This view resolver translates a view name to a URL and hands the request over to the RequestDispatcher to render the view.
Spring Web MVC Framework Examples:-
- Spring MVC Hello World Example
This example will explain how to write a simple Spring Web Hello World application. - Spring 3.0 MVC with Hibernate 3.0 CRUD Example using maven
Learn how to configure Spring 3 MVC with Hibernate 3 Using CRUD Operation in Spring MVC Framework.
Reference
Web MVC framework





No comments:
Post a Comment